Hiring independent contractors can be a strategic move for software companies looking to scale quickly while optimizing costs. However, misclassifying independent contractors as employees—or vice versa—can lead to severe financial, legal, and reputational consequences. In recent years, governments worldwide have tightened regulations to combat employment misclassification, imposing heavy fines and back taxes on businesses that fail to comply.
For tech startups and established software firms alike, understanding the associated-risks is critical. Employee misclassification penalties can include not only financial repercussions but also legal disputes and damage to a business’ reputation. Ultimately, the consequences of misclassifying employees as independent contractors can cripple a company’s growth.
This article explores the complexities of contractor misclassification, the penalties associated with it, and actionable strategies to ensure compliance.
What is Employee Misclassification?
Employee misclassification occurs when a company incorrectly classifies a worker as an independent contractor instead of an employee. In the software industry, where remote work and global hiring are common, the risk of misclassifying independent contractors is particularly high.
Many software company owners and HR professionals opt for contractors to reduce costs and streamline hiring. However, failing to classify workers correctly can lead to significant financial and legal consequences.
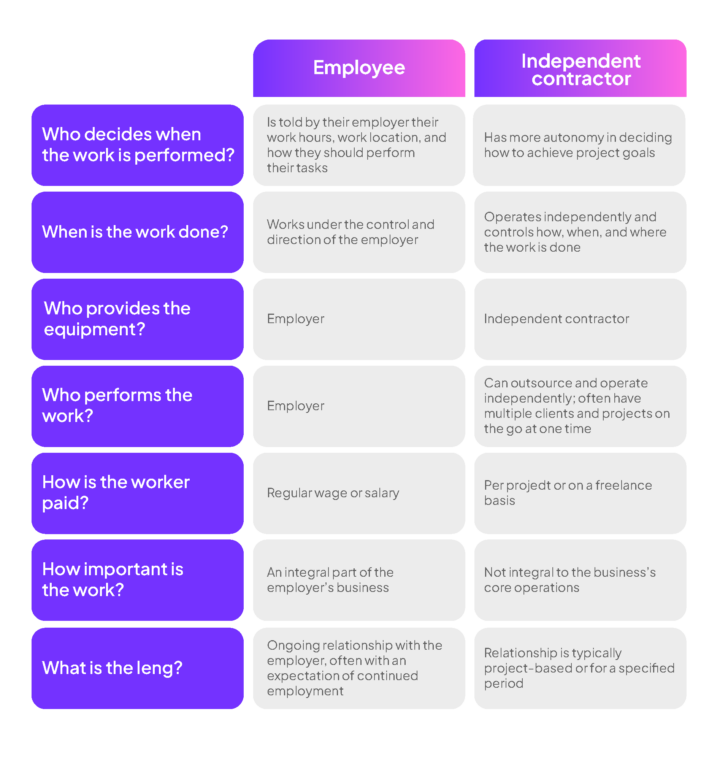
Understanding the Key Differences
To fully grasp the impact of employee misclassification, it is crucial to understand the fundamental differences between employees and independent contractors:
- Employees are under the control of the company in terms of work schedule, job responsibilities, and how tasks are performed. They typically receive benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, and retirement plans.
- Independent contractors work autonomously, set their own hours, and use their own tools and equipment. They are responsible for paying their own taxes and do not receive traditional employment benefits.
While independent contractors enjoy greater flexibility, the misclassification of independent contractors places companies at significant risk of audits, back taxes, fines, and potential lawsuits, which can severely impact financial stability and operational efficiency.
Why Does Contractor Misclassification Happen in Software Companies?
The nature of the software development industry makes it especially prone to employment misclassification. Many companies operate on a project-based model, hiring software engineers, developers, and IT professionals for short-term needs. Additionally, the prevalence of remote work and international hiring complicates compliance with various labor laws.
Software companies frequently misclassify employees due to several key factors:
- Lack of legal knowledge: Many software companies, especially startups and growing firms, lack dedicated HR teams with expertise in employment law.
- Misconceptions that freelancers or gig workers automatically qualify as independent contractors: Companies may assume that because software engineers or designers work on a per-project basis, they automatically qualify as independent contractors. However, if the company controls their workflow, assigns tasks directly, and sets expectations similar to full-time employees, misclassification occurs.
- Not considering changes: Some companies apply outdated classification models without considering changes in employment laws or workforce dynamics. Just because a role was historically classified as a contract position does not mean it still meets those legal requirements today.
- Efforts to reduce costs: Hiring contractors often seems more cost-effective since it eliminates expenses like benefits, taxes, and overtime pay.
- Poor communication with workers: Employees and contractors alike may be unclear about their classification status, especially when communication from HR or management is inconsistent. Clearly defining roles and responsibilities helps avoid disputes and misclassification claims.
- Different regulations across regions: Global software companies must navigate varying labor laws, which can be overwhelming without legal guidance. Compliance requirements differ between the U.S., Europe, Latin America, and Asia, increasing the risk of inadvertent misclassification.
- Industry-specific challenges: Software companies frequently use a mix of full-time employees and contractors, making classification more complex. Project-based work models, remote teams, and international hiring further complicate compliance.
Employee Misclassification Penalties
The consequences of misclassifying employees as independent contractors can be severe. Government agencies actively monitor and penalize companies that engage in misclassification.
Financial Penalties
One of the most immediate consequences of misclassification is the financial burden. Employers may be required to pay:
- Back wages and benefits: Employers must compensate misclassified workers for unpaid wages, overtime, and benefits they were entitled to receive.
- Unpaid taxes and withholding penalties: This includes payroll taxes, Social Security, Medicare contributions, and other government-mandated withholdings.
- Fines and interest: In many jurisdictions, employers face additional fines for failing to comply with classification regulations.
- Liquidated damages: In some cases, courts may require employers to pay additional compensation for damages caused by misclassification, such as unpaid breaks or denied benefits.
For example, in the U.S., the IRS imposes strict penalties on companies found guilty of misclassification. Depending on the severity of the case, businesses may be required to pay additional tax liabilities, penalties for failing to withhold income taxes, and potential criminal charges in cases of deliberate fraud.
Legal Consequences
Misclassification can lead to lawsuits from misclassified employees, resulting in settlements and legal fees. Workers who believe they have been wrongly classified may file claims with labor authorities, triggering audits and investigations that can expose compliance issues. Employee misclassification penalties can be severe, affecting not just finances but also a company’s long-term stability and ability to operate smoothly.
Software companies may face:
- Class-action lawsuits from multiple employees seeking unpaid wages and benefits.
- Government audits that can disrupt business operations and lead to further penalties.
- Injunctions and corrective actions requiring companies to adjust their employment practices.
- Potential bans on government contracts for companies found repeatedly violating employment laws.
Reputational Damage
Beyond financial and legal repercussions, contractor misclassification can severely impact a company’s reputation. Companies that violate labor laws may struggle to:
- Attract top talent—developers and IT professionals may hesitate to work for a company with a history of legal troubles.
- Secure partnerships and investments—non-compliance can deter investors and business partners.
- Maintain client relationships—clients who prioritize ethical business practices may sever ties with non-compliant vendors.
Operational Disruptions
If a misclassified employee seeks reclassification, companies may be forced to adjust their workforce structure, leading to operational disruptions. Businesses may experience:
- Delays in project timelines due to workforce restructuring.
- Increased administrative burden to ensure compliance moving forward.
- Higher costs associated with providing back pay, benefits, and legal fees.
Examples of Contractor Misclassification and Consequences
Understanding misclassification risks becomes clearer when examining real-world cases. Here are some notable misclassification lawsuits:
- Uber (2022): Paid $8.4 million in California to settle a class-action lawsuit over driver misclassification.
- Nike (2023): Faces potential fines and lawsuits exceeding $530 million for allegedly misclassifying thousands of workers worldwide.
- FedEx (2021): Paid $2.4 million in New Jersey after misclassifying 192 drivers. Previous lawsuits against FedEx have resulted in damages ranging from $5.3 million to $228 million.
- Arise Virtual Solutions (2023): Under DOL investigation for hiring over 22,000 workers as contractors without granting them full work autonomy.
- G&R Drywall and Framing (2021): Owner sentenced to nearly two years in prison for intentionally misclassifying 30 construction workers to evade taxes.
- Holland Services (2021): Paid almost $43.3 million in back wages and damages for misclassifying 700 employees.
Common Compliance Pitfalls in Software Development
Tech companies often make critical mistakes that increase the risk of misclassifying independent contractors, including:
- Exerting too much control over an independent contractor’s work schedule and tasks.
- Providing company equipment such as laptops and software access, which may indicate an employer-employee relationship.
- Misusing contract terms that suggest an ongoing, full-time relationship rather than a temporary, project-based arrangement.
Understanding the risk of misclassifying independent contractors is crucial for software companies looking to avoid compliance pitfalls and maintain sustainable growth. In the next section, we’ll explore actionable strategies to ensure proper worker classification and compliance with labor laws.
- Familiarize with local laws: Employment classification laws vary by region, so businesses operating across multiple countries must ensure compliance with jurisdiction-specific rules.
- Understand classification differences: Employers must differentiate between employees and independent contractors based on work control, tax obligations, and benefits eligibility.
- Consult legal counsel: Seeking legal or HR expert advice reduces the risk of misclassification penalties.
- Avoid excessive control: Contractors should maintain autonomy over their work schedules and methods to avoid classification as employees.
- Draft compliant contractor agreements: Clearly define the contractor’s responsibilities and scope of work while ensuring compliance with applicable labor laws.
- Regularly review worker status: Periodic classification audits help ensure compliance and catch potential misclassification issues early, including evolving labor laws and company needs.
Achieve Cost Efficiency and Compliance with LATAM’s Elite Talent – and BEON.tech
Employee misclassification is a serious risk that software companies cannot afford to overlook. Beyond financial penalties and legal repercussions, misclassification can damage a company’s reputation, disrupt operations, and hinder growth.
The good news is that partnering with a trusted provider like BEON.tech ensures businesses can scale efficiently while avoiding costly misclassification mistakes.
BEON.tech specializes in IT staff augmentation, ensuring that software companies can access top-tier talent while maintaining full compliance with labor laws.
With BEON.tech, business can:
- Ensure compliance while reducing costs by 10-20%
- Integrate top-tier talent from Latin America to their existing teams
- Avoid misclassification risks and forget about local employment law complexities.
- Benefit from a cost-efficient model that includes salaries, benefits, taxes, training, and payroll management without hidden fees.
- Work with the #1 Tech Talent Partner Worldwide (according to Clutch).
Our engagement model prioritizes an ongoing relationship, offering continuous feedback loops, hands-on support, and talent replacement at no additional cost to help you keep your team engaged and productive. Get in touch today.
Damian is a passionate Computer Science Major who has worked on the development of state-of-the-art technology throughout his whole life. In 2018, Damian founded BEON.tech in partnership with Michel Cohen to provide elite Latin American talent to US businesses exclusively.
Explore our
Why IT Team Augmentation is The Smart Way to Scale Your Development Team in 2025
The demand for skilled software developers continues to rise in 2025, leaving many companies struggling to fill critical roles. In fact, software development jobs are expected to grow by 17%. As technology evolves, CTOs face the challenge of scaling their teams efficiently while maintaining high-quality output. Traditional hiring processes are slow, expensive, and often fail…
IT Staff Augmentation vs. Direct Hire: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineering Leaders
For VPs of Engineering and other decision-makers, the choice between IT staff augmentation and direct hire can significantly impact your ability to scale, innovate, and meet project deadlines. Both hiring models offer unique advantages, but understanding their differences is key to making the right decision for your business. This blog post will explore the distinctions…
Engagement Models in Software Development: Which One Does Your Startup Need?
For startups looking to scale, hiring senior developers presents a unique set of challenges. Budget constraints, tight deadlines, and the need for specialized expertise can make it difficult to build an efficient development team in-house. This is where engagement models in software development become essential. An engagement model defines how your startup collaborates with external…






